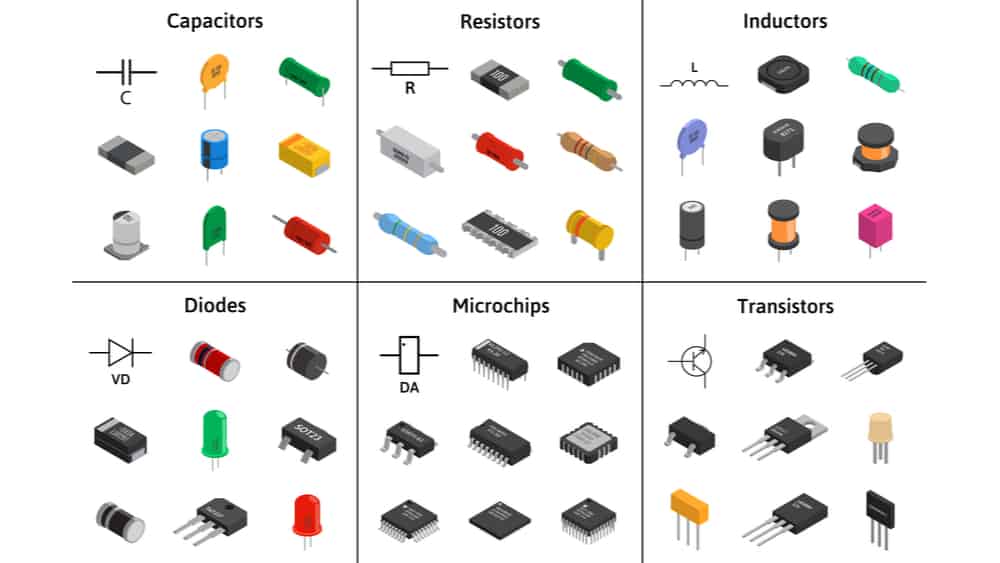
Embarking on the journey of circuit design requires a comprehensive understanding of the foundational electronic components that serve as the building blocks of any electrical system. As enthusiasts and engineers delve into this realm, the question arises: What are the main four electronic components used in a circuit? This exploration aims to dissect these essential components, shedding light on their roles, characteristics, and significance in creating functional and efficient electronic circuits.
1. Resistors: Managing Resistance and Current Flow
Resistors stand as fundamental components in circuitry, regulating the flow of electric current. They introduce resistance to the circuit, which is crucial for controlling the amount of current passing through other components. Resistors come in various values and are employed to set the operating conditions of transistors, LEDs, and other components within the circuit. Understanding resistor values, power ratings, and their impact on current flow is pivotal for circuit designers.
2. Capacitors: Storing and Releasing Electrical Energy
Capacitors play a crucial role in storing and releasing electrical energy within a circuit. They consist of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. Capacitors are utilized for smoothing voltage fluctuations, filtering signals, and timing circuits. Capacitance values, voltage ratings, and different types of capacitors, such as electrolytic and ceramic, influence their applications in diverse electronic systems.
3. Inductors: Creating Magnetic Fields for Energy Storage
Inductors, characterized by coils of wire, generate magnetic fields when an electric current flows through them. This property allows inductors to store energy in the form of a magnetic field. Inductors are vital in applications where energy storage and controlled release are essential, such as in power supplies and transformers. Understanding inductor properties, inductance values, and their impact on circuit behavior is key for effective circuit design.
4. Semiconductors (Transistors): Amplifying and Controlling Signals
Semiconductors, specifically transistors, are the heart of modern electronics, serving as amplifiers and signal controllers. Transistors can amplify weak signals, switch currents on and off, and form the basis of digital logic circuits. Understanding transistor configurations, such as NPN and PNP, and their applications in amplification and switching is critical for designing circuits ranging from audio amplifiers to digital processors.
Advanced Considerations: Beyond the Basics
While resistors, capacitors, inductors, and semiconductors form the core of electronic circuits, advanced considerations delve into integrated circuits (ICs), microcontrollers, and other specialized components. Integrated circuits, for example, combine multiple functions into a single package, streamlining circuit design and enhancing performance.
Conclusion: Crafting Precision in Circuitry
In conclusion, the main four electronic components – resistors, capacitors, inductors, and semiconductors – are the bedrock of circuit design, offering a diverse range of functionalities crucial for crafting precise and efficient electronic systems. Aspiring engineers and enthusiasts alike must delve into the intricacies of each component, understanding not only their individual properties but also their collective impact on the overall circuit behavior. Mastery of these foundational components empowers designers to innovate and create electronic systems that drive technological advancements in various fields.